Scenarios
Before starting the migration, you need to configure a target server. The target server is used to receive data from the source server. You can clone the target server for service testing, and launch the target server after you verify that your services can run properly on the target server.
Prerequisites
The migration is in the  stage and the status is Ready.
stage and the status is Ready.
Procedure
- Double-click the RDA icon on the desktop or RDA.exe in the installation directory to start the RDA client. Enter the username and password to log in to the RDA console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose SMS > Agents.
- In the server list, locate the source server to be migrated and click Configure in the Target column.
- On the Configure Basic Settings page, configure parameters by referring toTable 1.
Table 1 Basic parameter settings Parameter
Option
Description
Migration Template
N/A
After you select a migration template, the system automatically populates Network, Migration Rate Limit, Migration Method, Continuous Synchronization, Partition Resizing, Region, and Project based on the template. You can choose the default template created by the system or any one you created. For details, see Creating a Migration Template.
Network Type
Public
An EIP must be bound to the target server.
Network Type is set to Public by default.
Private
A Direct Connect connection, VPN connection, VPC peering connection, or VPC subnet must be provisioned. The private IP address of the target server will be used for migration.
Migration Rate Limit
N/A
You can configure the rate limiting based on the source bandwidth and service requirements.
If you do not want to limit the migration rate, set this parameter to 0.
NOTE:For a Linux migration, traffic limiting is done with Traffic Control (TC). If TC is not installed on the source server, the migration rate limit you configured here will not be applied during the migration.
Some Linux distributions do not support traffic limiting. For example, CentOS 8 and other CentOS 8-based distributions do not come with the TC module preinstalled.
Migration Method
Linux block-level
Migration and synchronization are performed by block. This method is efficient but the compatibility is poor.
Linux file-level
Migration and synchronization are performed by file. This method is inefficient, but the compatibility is excellent.
Windows block-level
Migration and synchronization are performed by block. For Windows servers, SMS only supports highly efficient block-level migration.
Continuous Synchronization
No
After the full replication, SMS will automatically launch the target server without synchronizing incremental data. To synchronize incremental data, you need to click Sync in the Operation column.
Yes
After a full replication, SMS will periodically synchronize incremental data. To complete the migration, you need to manually launch the target server.
Partition Resizing
No
The disk and partition settings from the source server will be retained on the target server.
Yes
You can resize disks and partitions on the target server. For details, see Resizing disks and partitions.
Start Target Upon Launch
No
Select this option to stop the target server after the migration is complete.
Yes
Select this option to start the target server after the migration is complete.
1. Select Yes for Partition Resizing and click Resize Partition. In the displayed dialog box, resize the disks and partitions on the target server as needed.Figure 1 Resizing disks and partitions (Windows)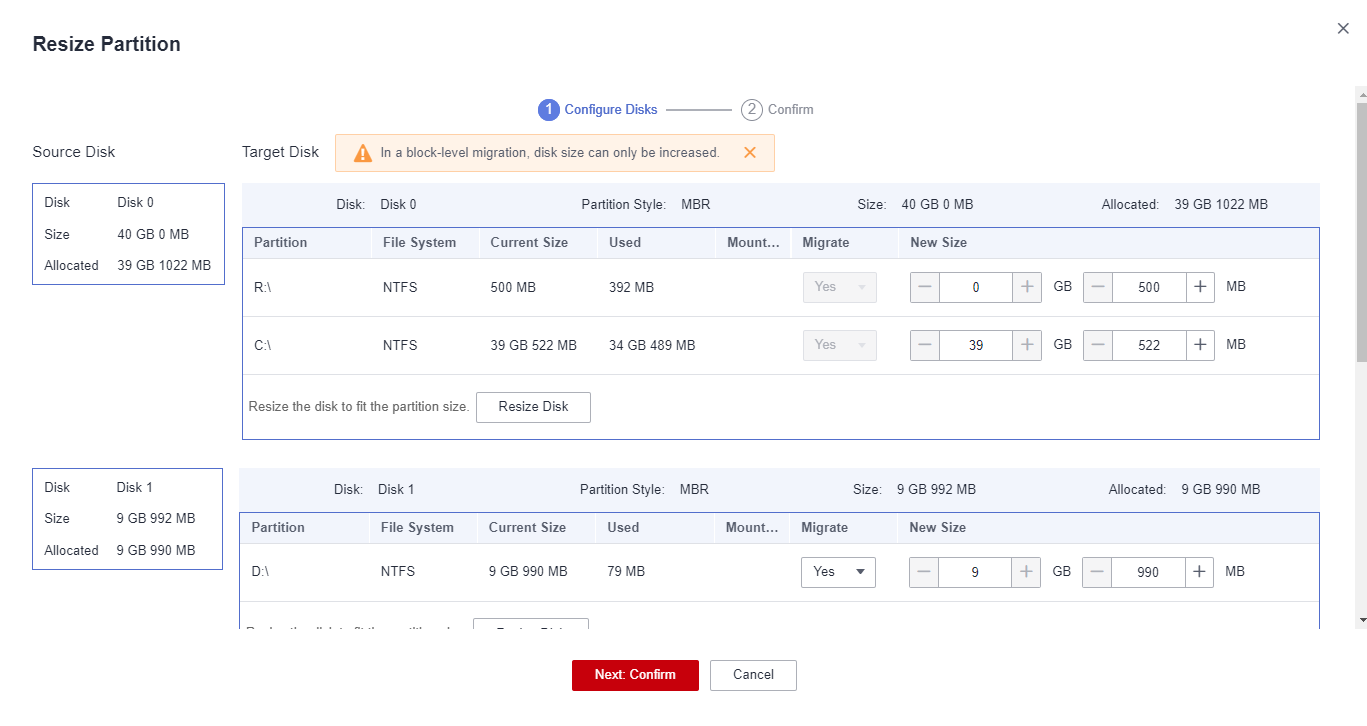 Figure 2 Resizing disks and partitions (Linux)
Figure 2 Resizing disks and partitions (Linux)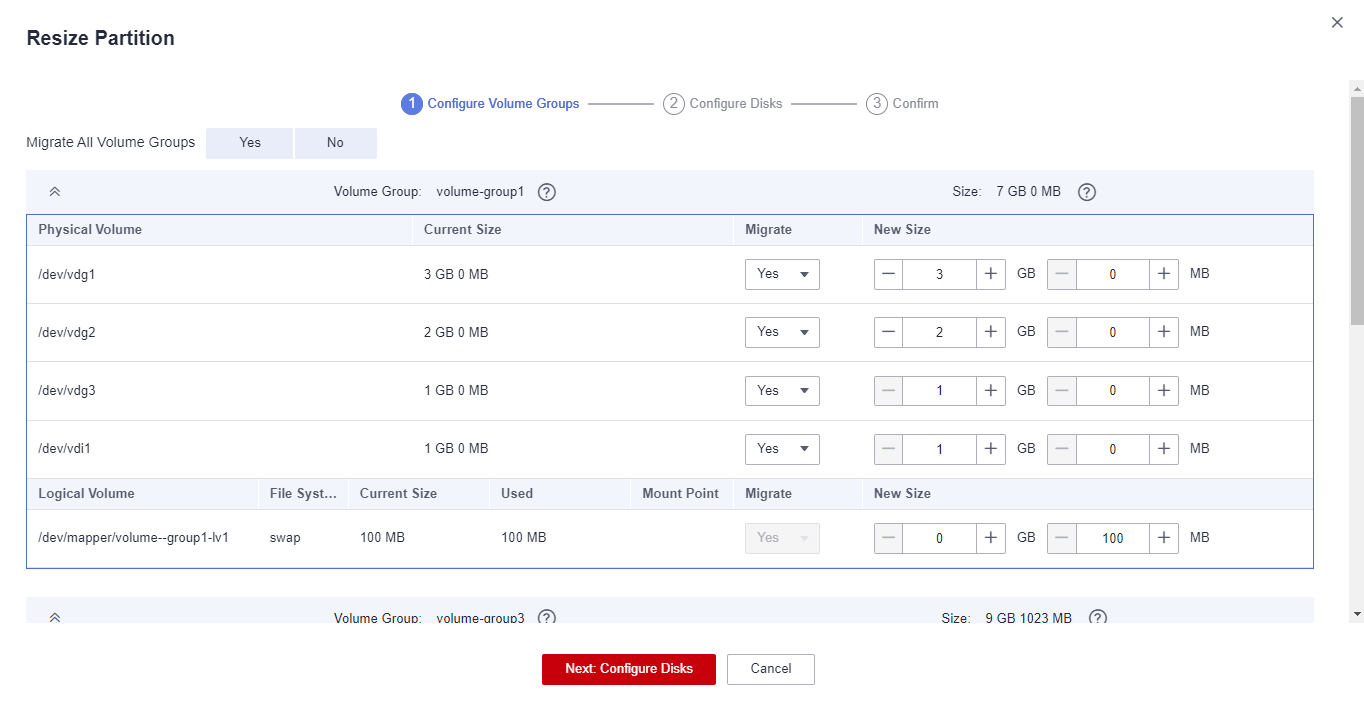
- You can choose whether to migrate source partitions and resize the paired target partitions.
- For a Linux server using LVM, you can choose whether to migrate physical or logical volumes and resize the paired target volumes.

- In a Windows migration, the system and boot partitions are migrated by default.
- In a Windows migration, you can increase the sizes of partitions, but you cannot reduce them.
- Partition resizing is not available for Btrfs partitions on Linux.
- In a Linux migration, the system and swap partitions are migrated by default.
- You can choose to migrate all or none volume groups by configuring Migrate All Volume Groups.
- If you choose to migrate none of the logical volumes in a volume group, their physical volumes will not be migrated by default.
- In a Linux block-level migration, you can increase the size of a partition, but you cannot decrease it.
- In a Linux file-level migration, you can increase or decrease partition size. The new partition size must be at least 1 GB larger than the used partition space. If the current partition size is not 1 GB larger than the used partition space, the partition size cannot be decreased.
- If the total partition size after resizing is larger than the disk size, you need to expand the disk capacity to fit the partition size.
- If the total partition size after resizing is much smaller than the disk size, you can decrease the disk size as needed.
2. Click Next: Configure Disks. Resize the disks as needed. Then confirm the configurations and click OK.

After you click OK, the setting of Partition Resizing cannot be changed. If you want to restore the disk partition settings as they were, locate the source server to be migrated and choose More > Delete in the Operation column. Then restart the Agent on the source server, configure a target server again, and set Partition Resizing to No.
- Click Next: Configure Target in the lower right corner.
- On the Configure Target page, set parameters as prompted.
Table 2 Parameters for configuring a target server Parameter
Option
Description
Region
N/A
- Select a region where the target server is to be provisioned from the drop-down list.
- Consider your service requirements when selecting a region.
Project
N/A
- Select a project in the region from the drop-down list.
- You can select a project only after selecting a region.
Server
Use existing
Select an existing server based on the recommended target server specifications above the server list. For details, see Use existing.
Create new
Configure VPC, Subnet, Security Group, and the parameters in Advanced Settings. For details, see Create new.
- Use existingThe target server must meet requirements listed below. If no existing server meets the requirements, click Buy Now to create one based on the recommended specifications. For details, see Purchasing an ECS.
Source servers can be migrated to pay-per-use or yearly/monthly ECSs. You can select ECSs of whichever billing mode is appropriate.
- A target server running Windows must have at least 2 GB of memory.
- A target server must have at least as many disks as the source server, and each disk on the target server must be at least the size recommended by the system.
- A target server must run the same type of OS as the source server, or there will be a server name conflict.
- A target server must be reachable for the source server. An EIP must be configured for the target server, or a VPN or Direct Connect connection must be established between the source and target.
- The security group of the VPC that a target server is in must be correctly configured. It must be configured to allow access on TCP ports 8899, 8900, and 22 for a Windows migration, on ports 8900 and 22 for a Linux block-level migration, or on port 22 for a Linux file-level migration.

- For security purposes, these ports are only opened to the source server.
- The firewall of the target server must allow traffic to these ports.
- Create new
- If you select Recommended for Server Template, the VPC, subnet, and security group will be automatically created. You can change the settings as needed.The server name, AZ, specifications, system disk, data disk and EIP in advanced settings are automatically configured. You can modify the settings as needed.Figure 3 Recommended
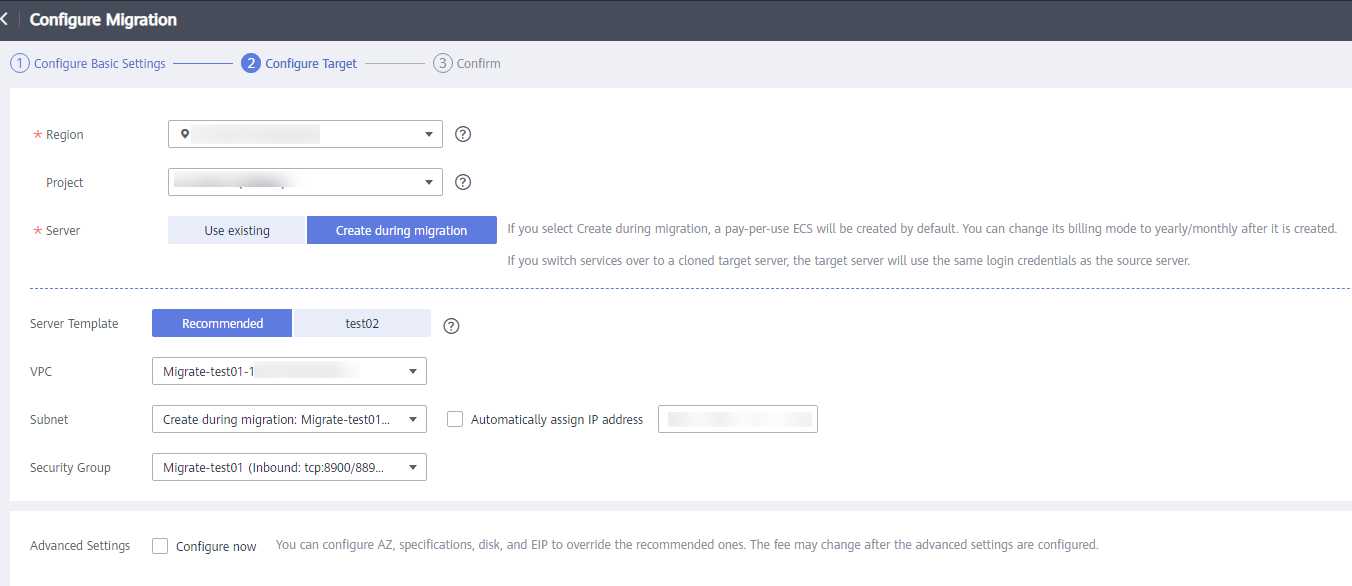 Figure 4 Advanced Settings
Figure 4 Advanced Settings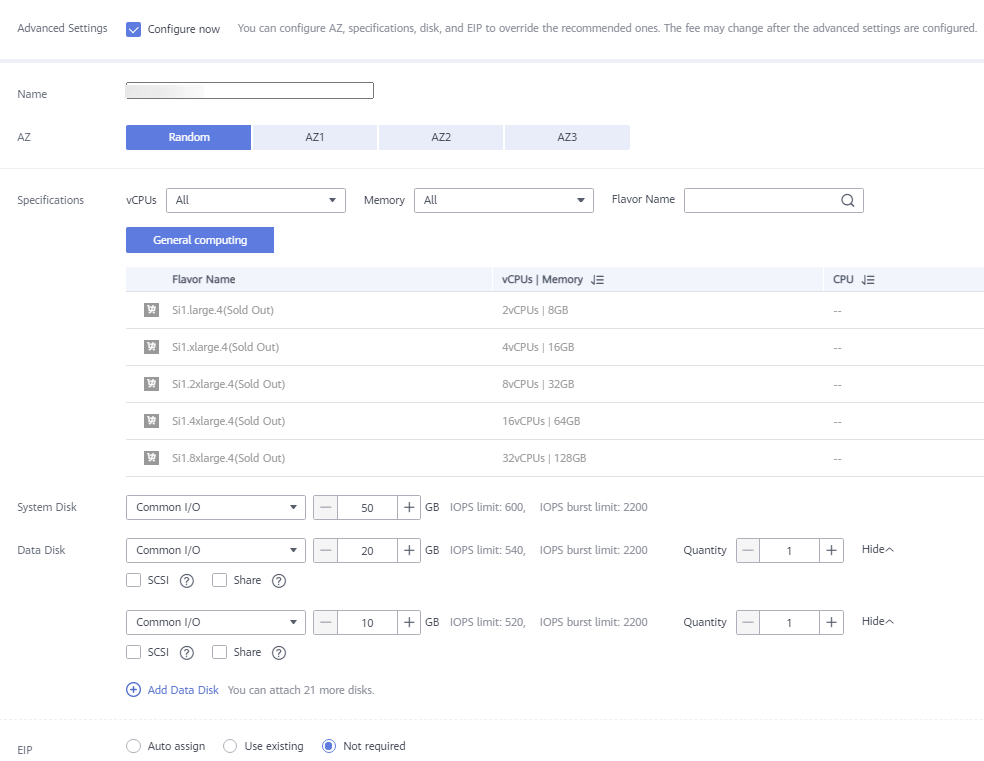
- Data disks must be either VBD or SCSI. VBD is the default device type for data disks.
- Data disks can be created as shared disks.
- If you select an existing template, the VPC, subnet, security group, AZ, and disk will be configured based on the template. You can change the configurations as needed. To learn how to create a server template, see Creating a Server Template.
 If you select Recommended for Server Template, SMS will automatically:
If you select Recommended for Server Template, SMS will automatically:- Create a VPC and subnet.
If the source IP address is 192.168.X.X, SMS creates a VPC and a subnet that both belong to the network segment 192.168.0.0/16.
If the source IP address is 172.16.X.X, SMS creates a VPC and a subnet that both belong to the network segment 172.16.0.0/12.
If the source IP address is 10.X.X.X, SMS creates a VPC and a subnet that both belong to the network segment 10.0.0.0/8.
- Create a security group and allow ports based on the service requirements: ports 8899, 8900, and 22 for a Windows migration, ports 8900 and 22 for a Linux block-level migration, or port 22 for a Linux file-level migration.
- Create a VPC and subnet.
- If you select Recommended for Server Template, the VPC, subnet, and security group will be automatically created. You can change the settings as needed.
- Click Next: Confirm in the lower right corner.Figure 5 Confirming the configuration
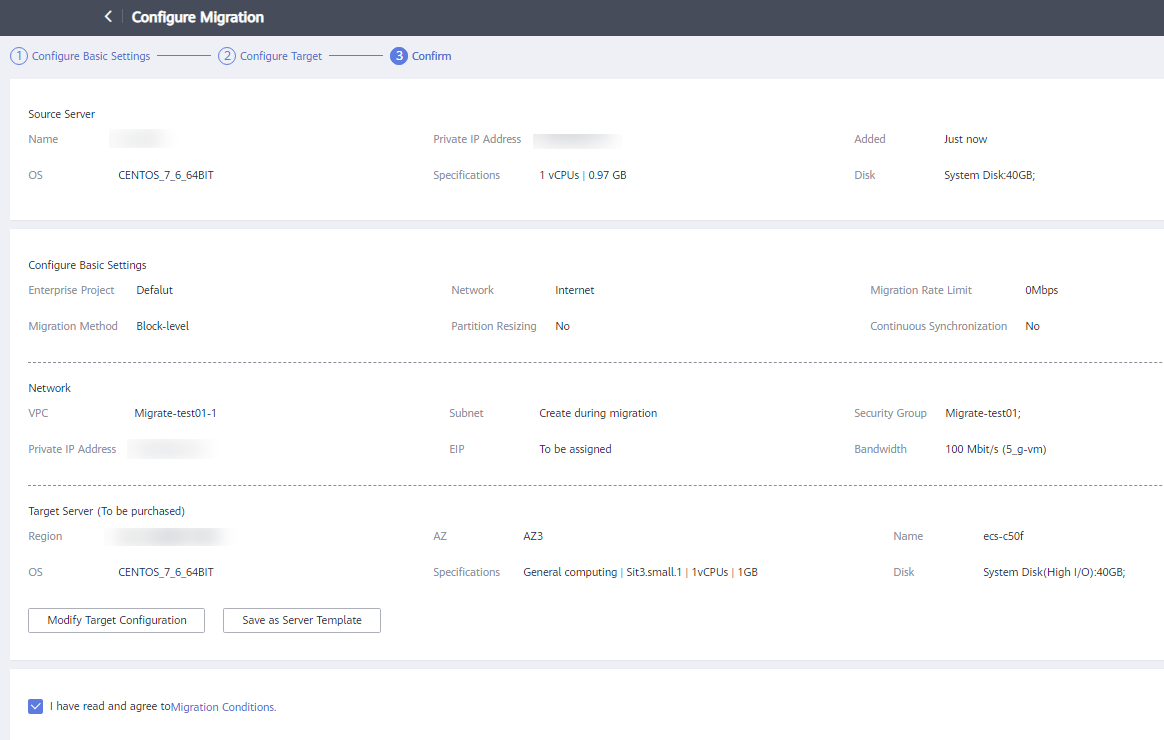
- (Optional) Click Save as Server Template. In the displayed Create Server Template dialog box, enter a template name and click OK to save the target configuration as a template.
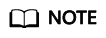
Save as Server Template is available only when you set Server Template to Recommended.
Figure 6 Create Server Template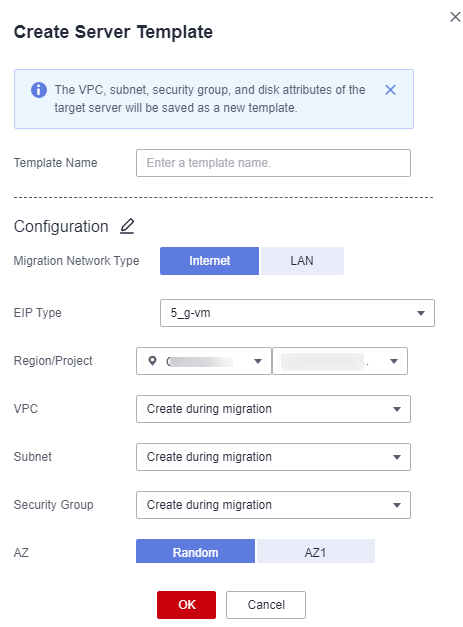
- After you confirm that the configuration is correct, click Save. In the displayed dialog box, read the migration conditions and click Yes.If you want to start the migration immediately, click Save and Start. In the displayed dialog box, read the migration conditions and click Yes.Figure 7 Saving configuration
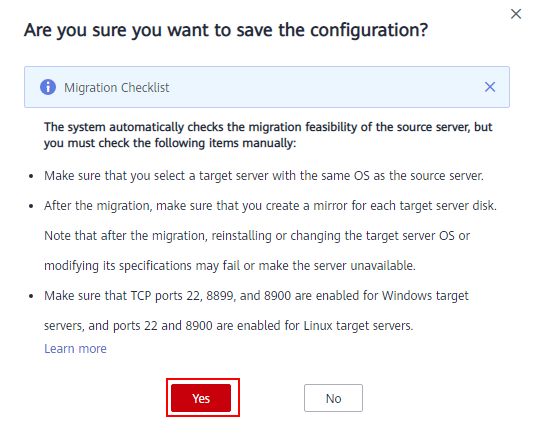 Figure 8 Saving configuration and starting migration
Figure 8 Saving configuration and starting migration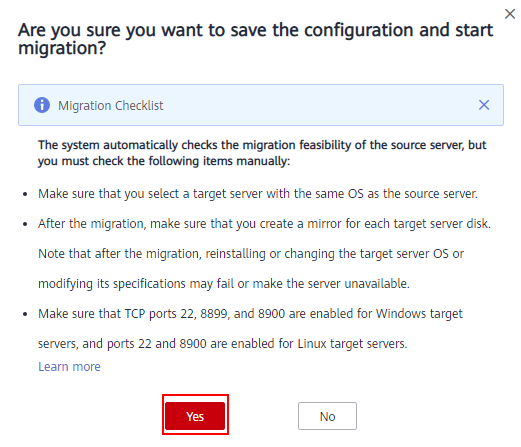
If
 is displayed in the Migration Stage column, the target server has been configured.
is displayed in the Migration Stage column, the target server has been configured.